AsyncStorage chỉ đơn giản là lưu dữ liệu vào tài liệu trên ổ cứng của điện thoại và do đó bất kỳ ai có quyền truy cập vào hệ thống tệp của điện thoại đều có thể đọc dữ liệu đó. Ít nhất là trên iOS dữ liệuứng dụng nào chỉ ứng dụng đó xem được (chính sách sandboxing) của Apple.

Bước 1: Trình bày
Trong bước này, chúng ta sẽ tạo tệp App.js.
import React from 'react' import AsyncStorageExample from './async_storage_example.js' const App = () => { return ( <AsyncStorageExample /> ) } export default App
Bước 2: Logic
name từ trạng thái ban đầu là chuỗi rỗng. Chúng tôi sẽ cập nhật nó từ bộ lưu trữ liên tục khi thành phần này được gắn kết.
setName sẽ lấy văn bản từ trường đầu vào của chúng ta, lưu nó bằng AsyncStorage và cập nhật trạng thái.
async_storage_example.js
import React, { Component } from 'react' import { StatusBar } from 'react-native' import { AsyncStorage, Text, View, TextInput, StyleSheet } from 'react-native' class AsyncStorageExample extends Component { state = { 'name': '' } componentDidMount = () => AsyncStorage.getItem('name').then((value) => this.setState({ 'name': value })) setName = (value) => { AsyncStorage.setItem('name', value); this.setState({ 'name': value }); } render() { return ( <View style = {styles.container}> <TextInput style = {styles.textInput} autoCapitalize = 'none' onChangeText = {this.setName}/> <Text> {this.state.name} </Text> </View> ) } } export default AsyncStorageExample const styles = StyleSheet.create ({ container: { flex: 1, alignItems: 'center', marginTop: 50 }, textInput: { margin: 5, height: 100, borderWidth: 1, backgroundColor: '#7685ed' } })
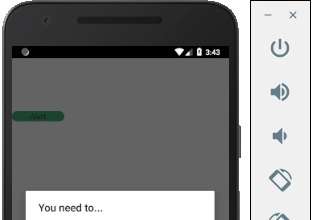
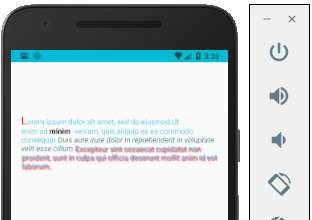
Khi chạy ứng dụng, có thể cập nhật văn bản bằng cách nhập vào trường nhập liệu.